What are the main management rules for private applications on Android?
This tutorial introduces you to the concepts you need to know and the main management rules for private applications on Android, and also shows you how to see if an error occurred while updating your private application.
A. Concepts to Know
1. Package Name
The package name of an application is its unique Android identifier. Two applications cannot have the same package name; otherwise, they will be considered a single application by the devices. This is why the Private Play Store does not allow the addition of a private or public application whose package name is already known to their services. From the TinyMDM Store, you can add an application whose package name is known to the Play Store, but only if the application has not already been approved from another store. Indeed, if the same application (same package name) is approved from two different stores on your console (the Play Store and the TinyMDM Store, for example), both stores will attempt to install the same application on the device, which creates a conflict, even if they are two different versions.
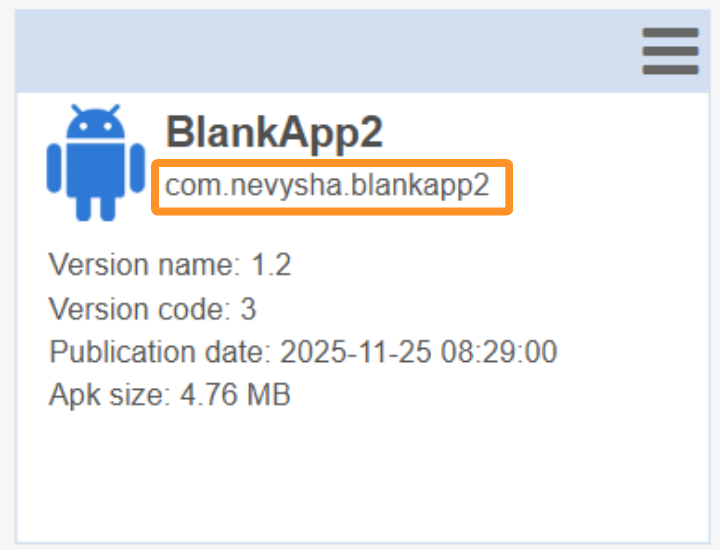
Where to find the package name on TinyMDM?
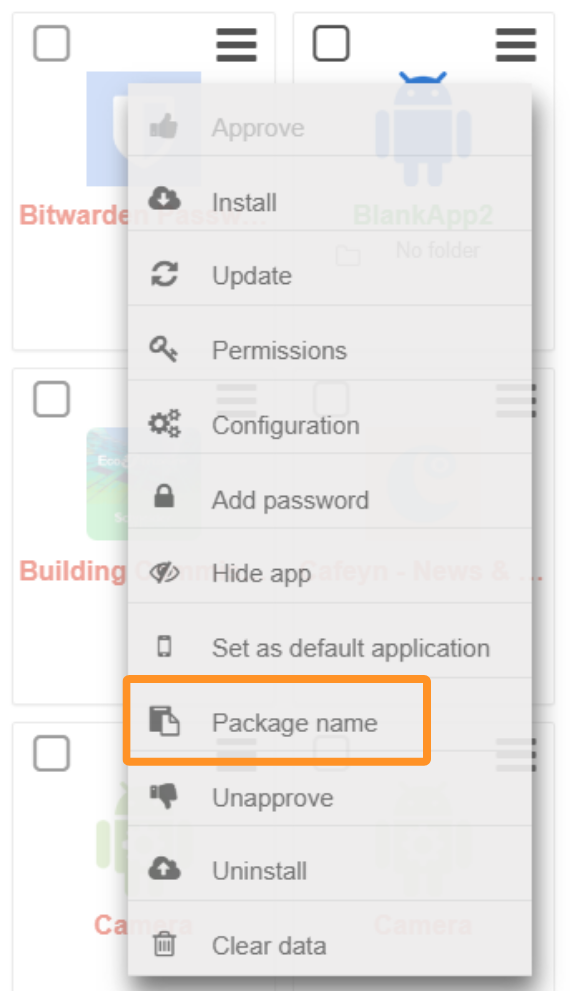
The package name for all applications is accessible from the Policies tab. To access it, open the desired policy, then:
- Expand the Apps Management subtab
- Click on the menu for the desired application
- Select Package Name
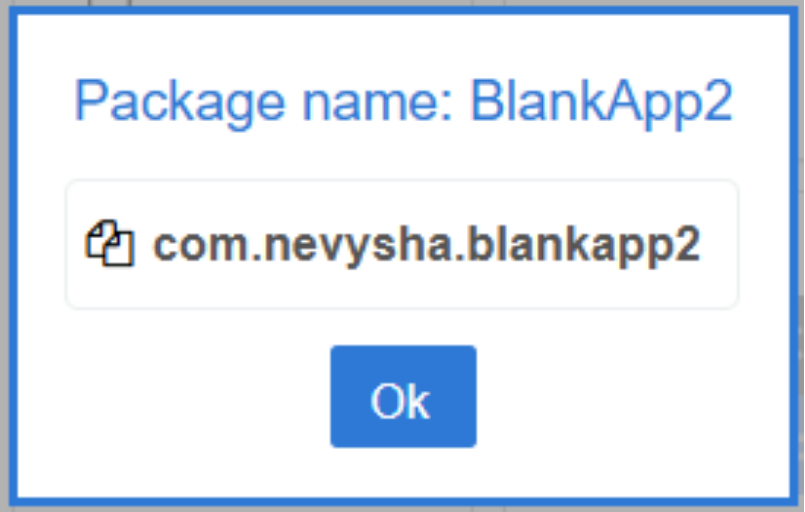
How to use the package name on TinyMDM?
From the TinyMDM console, an application’s package name is used to recognize the application in the TinyMDM Store or the Private Play Store.

It is also used to configure certain options in the Advanced apps management menu of the policy. For example, it is possible to exclude applications from the most-used apps pane in kiosk mode using their package name.
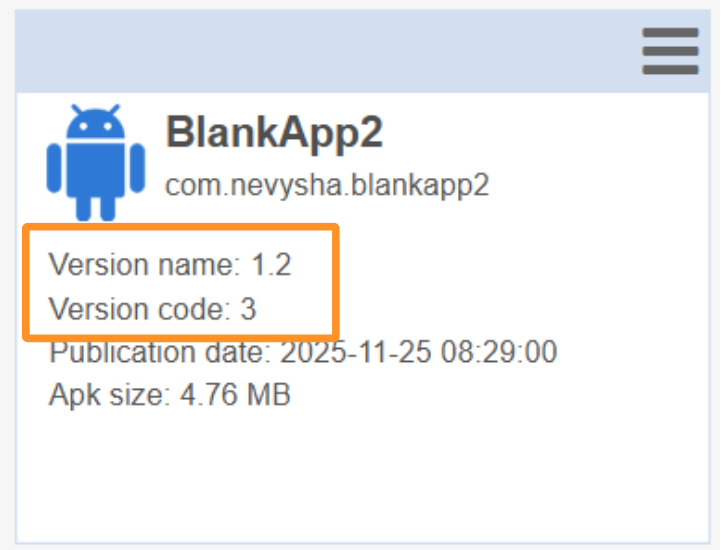
2. The Version Code and Version Name
Every Android application has two version identifiers: the version name and the version code. Both are defined by the application developer:
- The version name has no specific restriction; it can contain numbers and letters, and its modification is not mandatory.
- The version code, however, must be a number and must be incremented with every new version.
B. Updating a Private Application
1. Have an identical package name
For an application to be updated, the package name of the new version must be identical to that of the previous version so that the device’s Android system recognizes that it is indeed the same application and initiates the update.
2. Have a version code strictly greater than the previous one
When updating an application, the version code of the update APK file must be strictly greater than that of the version installed on the device (previous version). Indeed, on Android, downgrading, meaning installing a lower version over a higher version, is not permitted. If an application version with a version code equal to or lower than the version currently installed on the device attempts to be installed, the update will not work.
3. Have a signed APK file
For an application to be installed on an Android device, its APK file must be signed. For an update, the update APK must be signed with the same signature as the APK of the previous version. If this is not the case, even if the package name is identical and the version code is strictly greater, the application will not update.
C. In case of errors
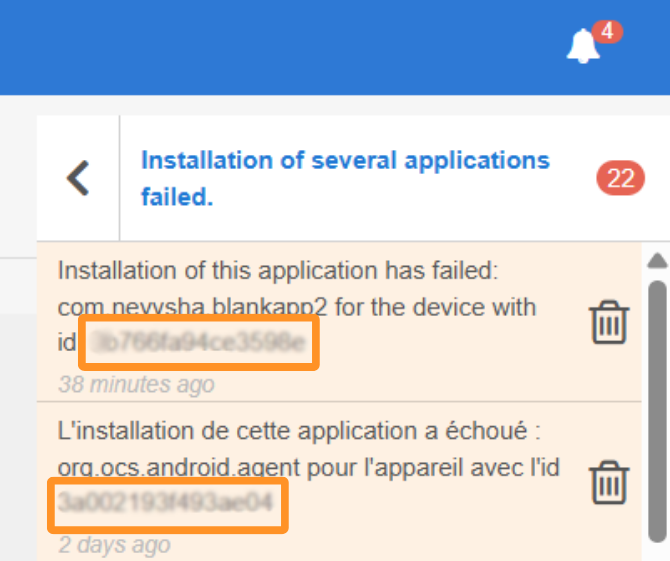
If an error occurs during the installation or update of a TinyMDM Store application, a notification will be displayed in your console. To find the device concerned by the error and understand what triggered it, simply open the notification bell, located at the top right of your administration console:

Then copy the ID of the device concerned by the error:
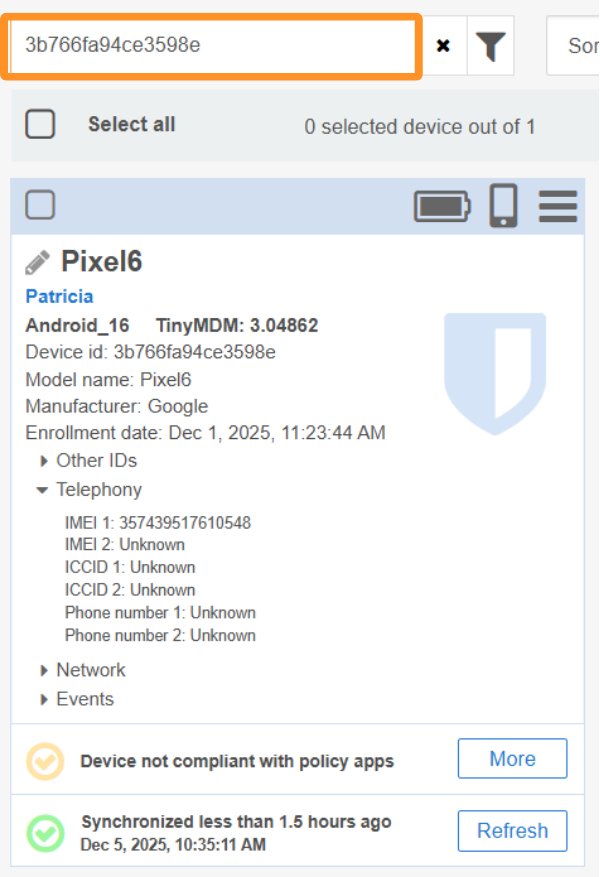
Then open the Devices tab and paste the identifier into the search bar to make the concerned device appear and click on More.
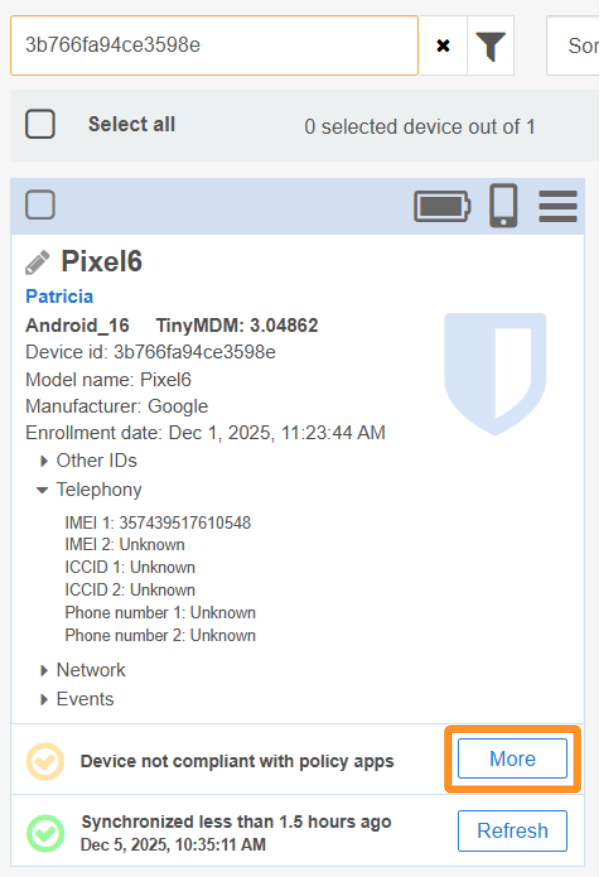
Then, in the window that opens, click on See details:
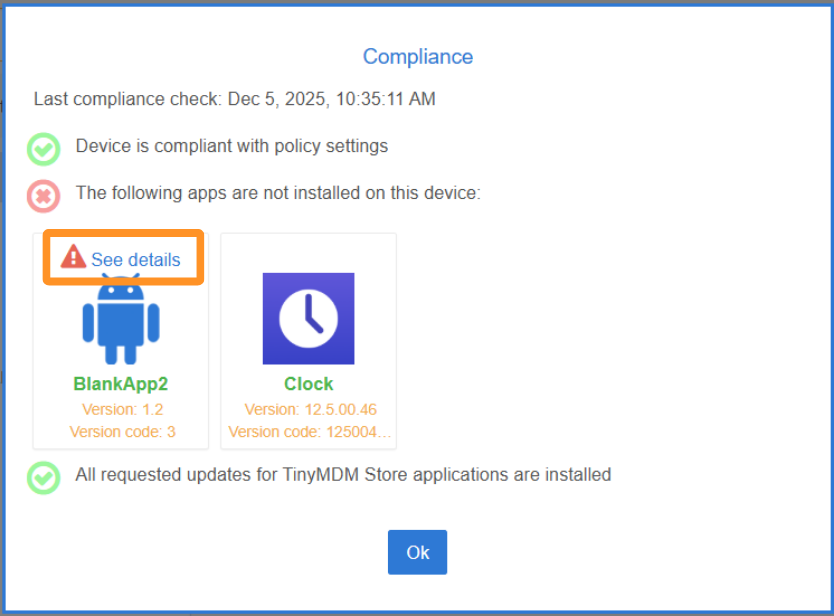
The error below is an error that originates from the device’s Android system, not from TinyMDM. If it is not explicit, feel free to perform a web search to find out its meaning:
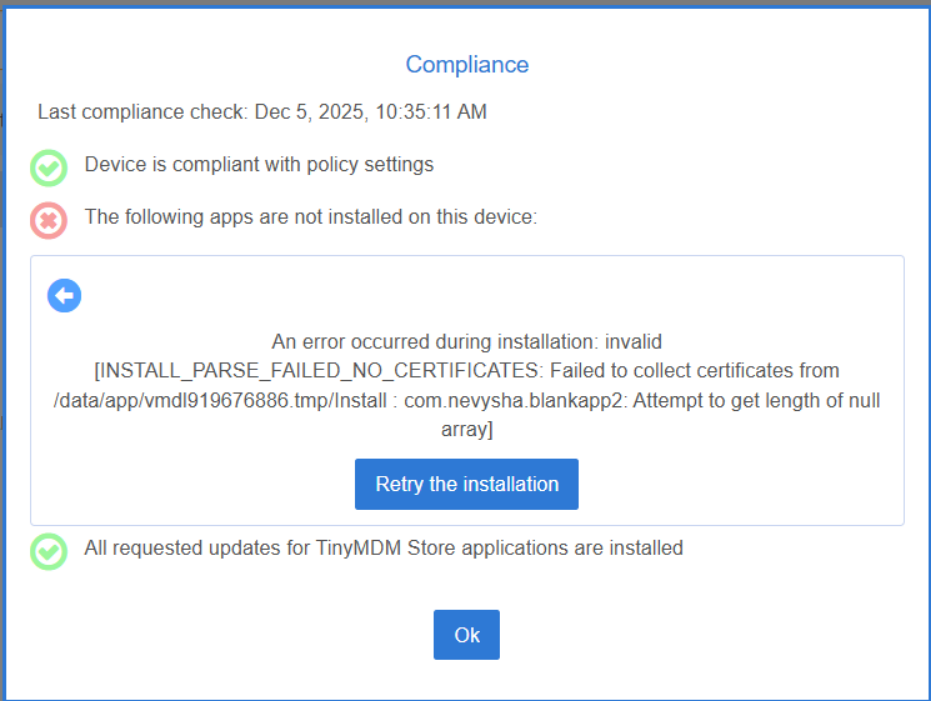
In summary:
- The package name allows you to identify your private application; it must be unique on your TinyMDM console.
- Each version of your private application has a version code that allows it to be identified.
- Your private application must be signed to be installed on your devices.
The following elements are necessary for your private application to be updated:
- Identical package name
- Strictly higher version code
- Identical signature
